Book an Appointment
Gum Surgery
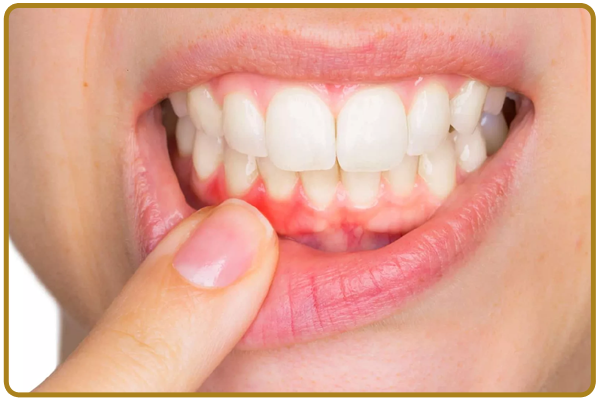
Gum Surgery
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease refers to inflammation of the soft tissue (gingiva) and abnormal loss of bone that surrounds the teeth and holds them in place. Gum disease is the second most common cause of toothache.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is caused by toxins secreted by bacteria inplaque that accumulate over time along the gum line. This plaque is a mixture of food, saliva, and bacteria.
What Are Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Early symptoms of gum disease include gum bleeding without pain. Pain is a symptom of more advanced gum disease as the loss of bone around the teeth leads to the formation of gum pockets. Bacteria in these pockets cause gum infection, swelling, pain, and further bone destruction. Advanced gum disease can cause loss of otherwise healthy teeth.
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
Treatment of early gum disease involves oral hygiene and removal of bacterial plaque. Moderate to advanced gum disease usually requires a thorough cleaning of the teeth and teeth roots called root planing and subgingival curettage.Root planing is the removal of plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) from exposed teeth roots while subgingival curettage refers to the removal of the surface of the inflamed layer of gum tissue. Both of these procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia and may be accompanied by the use of oral antibiotics to overcome gum infection or abscess. Follow-up gum treatment may include various types of gum surgeries or flap surgeries.
Get In Touch
Tags
- Precious 32 Dental
- Precious 32 Dental Gurugram
- Precious 32 Dental Gurugram Sector 46
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 44
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 44
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 44
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 44
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 44
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 44
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 44
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 44
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 44
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 44
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 44
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 44
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 44
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 44
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 44
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 44
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 44
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 44
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 44
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 45
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 45
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 45
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 45
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 45
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 45
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 45
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 45
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 45
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 45
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 45
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 45
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 45
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 45
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 45
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 45
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 45
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 45
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 45
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 46
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 46
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 46
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 46
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 46
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 46
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 46
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 46
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 46
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 46
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 46
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 46
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 46
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 46
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 46
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 46
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 46
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 46
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 47
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 47
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 47
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 47
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 47
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 47
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 47
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 47
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 47
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 47
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 47
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 47
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 47
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 47
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 47
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 47
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 47
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 47
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 47
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 48
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 48
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 48
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 48
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 48
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 48
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 48
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 48
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 48
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 48
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 48
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 48
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 48
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 48
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 48
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 48
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 48
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 48
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 48
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 49
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 49
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 49
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 49
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 49
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 49
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 49
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 49
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 49
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 49
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 49
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 49
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 49
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 49
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 49
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 49
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 49
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 49
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 49
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 50
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 50
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 50
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 50
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 50
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 50
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 50
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 50
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 50
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 50
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 50
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 50
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 50
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 50
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 50
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 50
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 50
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 50
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 50
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Dentist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram Sector 51
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 51
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram Sector 51
- Dental Implant in Gurugram Sector 51
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram Sector 51
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram Sector 51
- General Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 51
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram Sector 51
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 51
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 51
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram Sector 51
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram Sector 51
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram Sector 51
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Dental Implants in Gurugram Sector 51
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram Sector 51
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram Sector 51
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram Sector 51
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram Sector 51
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram Sector 51
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram Sector 65
- OSMF Treatment in Gurugram
- OSMF Treatment Specialist in Gurugram
- Best Dental Clinic in Gurugram
- Best Dentist in Gurugram
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation Specialist in Gurugram
- Best Prosthodontist in Gurugram
- Best Implantologist in Gurugram
- Best Oral Surgeon in Gurugram
- Best Maxillofacial Surgeon in Gurugram
- Best Orthodontist in Gurugram
- Best Pedodontist in Gurugram
- Preventive Dentistry Specialist in Gurugram
- Single Sitting Root Canal Treatment in Gurugram
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation in Gurugram
- Veneers Specialist in Gurugram
- Smile Designing Treatment in Gurugram
- Implant Supported Prosthesis in Gurugram
- Maxillofacial Prosthesis in Gurugram
- Dental Implant in Gurugram
- Facial Trauma Treatment in Gurugram
- TMJ Treatment Specialist in Gurugram
- Self Ligating Orthodontic Treatment in Gurugram
- Rotary Endodontic Treatment for Children in Gurugram
- General Dentistry in Gurugram
- Missing Teeth Replacement in Gurugram
- Cosmetic Dentistry in Gurugram
- Kids Dentistry in Gurugram
- Teeth Alignment Treatment in Gurugram
- Surgical Dentistry in Gurugram
- Dental Fillings in Gurugram
- Single Sitting RCT in Gurugram
- Teeth Cleaning treatment in Gurugram
- Teeth Sensitivity Treatment in Gurugram
- Oral Splint Treatment in Gurugram
- Dental Implants in Gurugram
- Teeth Whitening Treatment in Gurugram
- Fluoride Therapy in Gurugram
- Pediatric Dental Care in Gurugram
- Braces Treatment in Gurugram
- Aligner Treatment in Gurugram
- Wisdom Tooth Removal in Gurugram
- Gum Surgery in Gurugram
- show more
- show less









